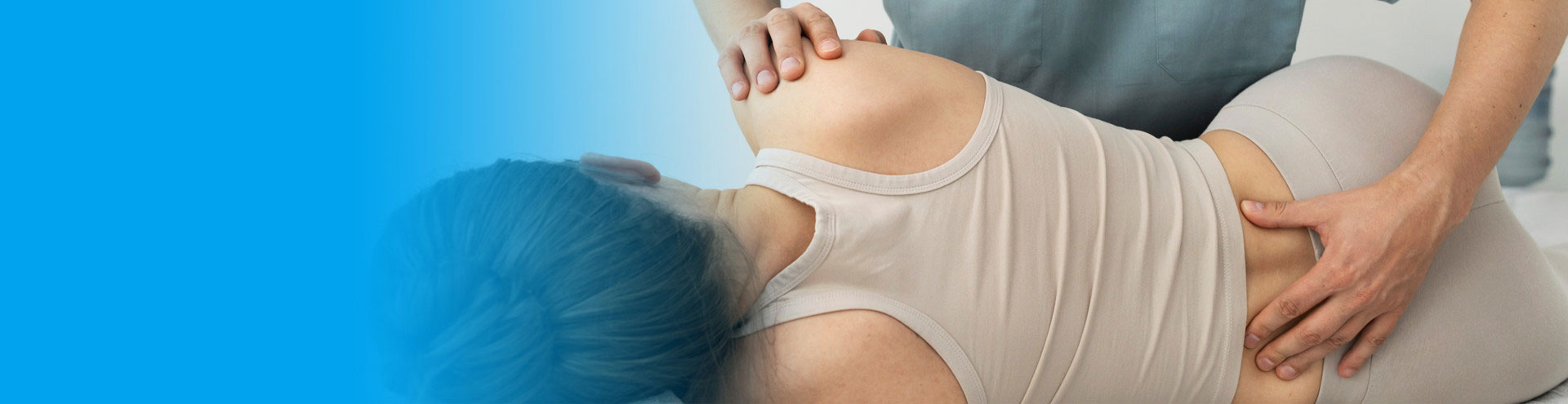
Chiropractic is a healthcare profession concerned with the diagnosis, care, and management of mechanical disorders of the neuromusculoskeletal system, as well as the effects of these disorders on the function of the nervous system and general health.
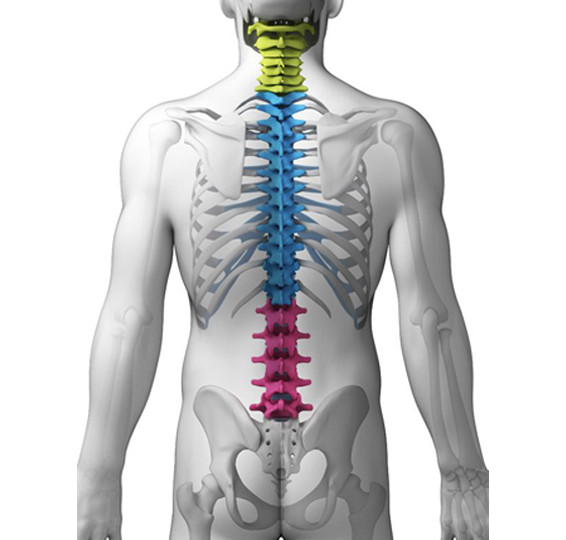
Chiropractic management includes manual and safe adjustments of joints, and may include soft-tissue and other relevant adjunct therapies.
Manual procedures, including gentle spinal adjustments, other joint manipulations, and soft-tissue techniques are important procedures typically used by chiropractors, but these may not exclude other potential procedures. Chiropractic is scientifically based, building on rigorous training in accredited chiropractic institutions, accumulated clinic experience and existing best available evidence. The explanation of disorders may not always necessarily result in chiropractic care as described above, but may lead to advice alone, instructions, or recommendations for other types of management or procedures.
The Chiropractic Association (Singapore) believes that the chiropractic profession is a mainstream healthcare discipline, with the ability to provide primary contact healthcare.
You may refer to more about chiropractic on the World Federation of Chiropractic website at https://www.wfc.org/what-is-chiropractic
Chiropractic Identity
The spinal health care experts in the health care system
therefore possessing:
- Ability to potentially improve function in the neuromusculoskeletal system, as well as overall health, well-being and quality of life
- Specialised approach to examination, diagnosis and management, based on best available research and clinic evidence with particular emphasis on the relationship between the spine and the nervous system
- Tradition of effectiveness and patient satisfaction
- Conservative management without the use of drugs or surgery, enabling patients to avoid these where possible but also having the ability to refer for medical management
- Expertly qualified providers of spinal adjustments, manipulation and other manual care, as well as exercise instructions and patient education
- Collaboration with other health professionals
- A patient-centered and biopsychosocial approach, emphasizing the mind/body relationship in health, the self-healing potential of the individual, as well as individual responsibility for health and encouraging patient independence